By: Ganesha Loree
Geovis Project Assignment, TMU Geography, SA8905, Fall 2025
INTRODUCTION
`Chicago is considered the most gang-occupied city in the United States, with 150,000 gang-affiliated residents, representing more than 100 gangs. In 2024, 46 gangs and their boundaries across Chicago were mapped by the City of Chicago. Factors about the formation of gangs have been of interest and a topic of research for many years all over the world (Assari et al., 2020), but for the purpose of this project, these factors are going to stem from demographics of Chicago. For instance, Chicago has deep roots within gang history and culture. Not only gangs but violent crimes are also dense. Demographics such as income, education, housing, race, etc., play factors within the neighbourhoods of Chicago and could be part of the cause of gang history.
METHODOLOGY
Step 1: Data Preparation
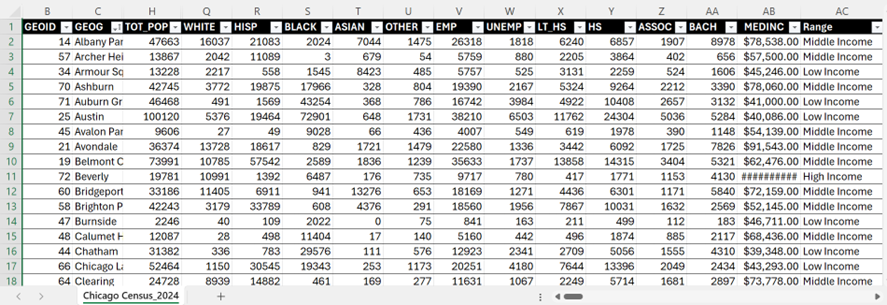
Chicago Neighbourhood Census Data (2025): Over 200 socioeconomic and demographic data for each neighbourhood was obtained from the Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning (CMAP) (Figure 1). In July 2025 their Community Data Snapshot portal released granular insights into population characteristics, income levels, housing, education, and employment metrics across Chicago’s neighbourhoods.
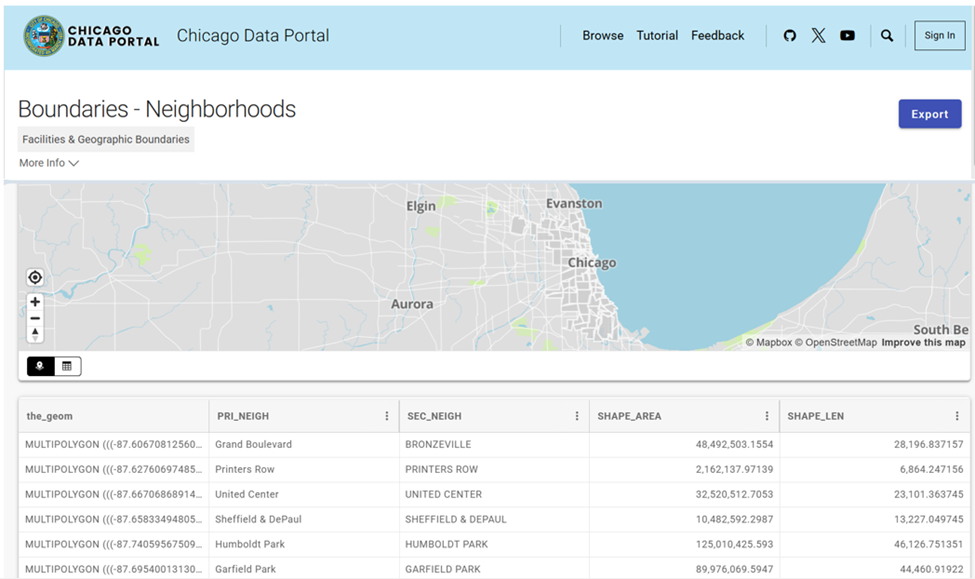
Chicago Neighbourhood Boundary Files: official geographic boundaries for Chicago neighbourhoods were downloaded from the City of Chicago’s open data portal (Figure 2). These shapefiles were used to spatially join census data and support geospatial visualization.
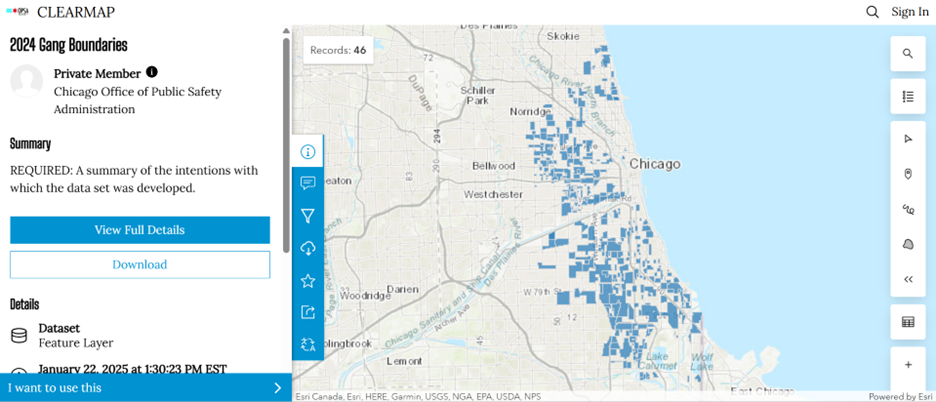
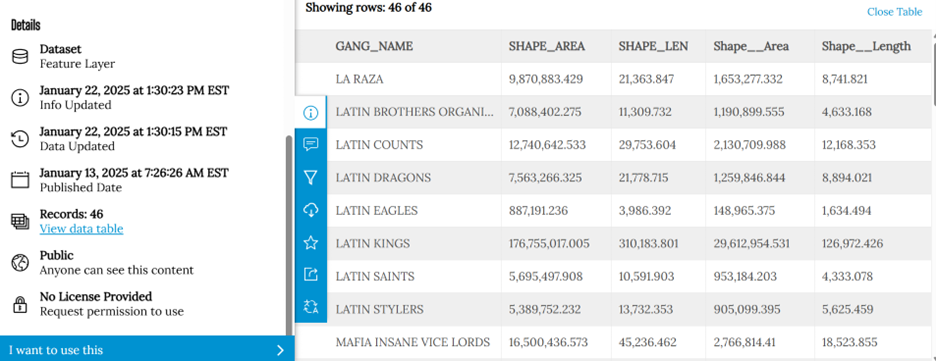
Chicago Gang Territory Boundaries (2024): Gang territory data from 2024 was sourced from the Chicago Police Department’s GIS portal (Figure 3). These boundaries depict areas of known gang influence and were integrated into the spatial database to support comparative analysis with neighbourhood-level census indicators.
Step 2: Technology
Once the data was downloaded, they were applied to software to visualize the data. A combination of technologies was used, ArcGIS Pro and Sketchup (Web). ArcGIS Pro was used to import all boundary files, where neighbourhood census data was joined to Chicago boundary shapefile using unique identifier such as Neighbourhood Name (Figure 4).
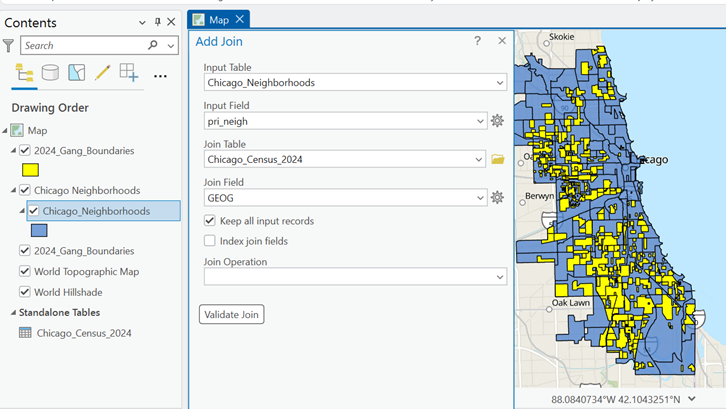
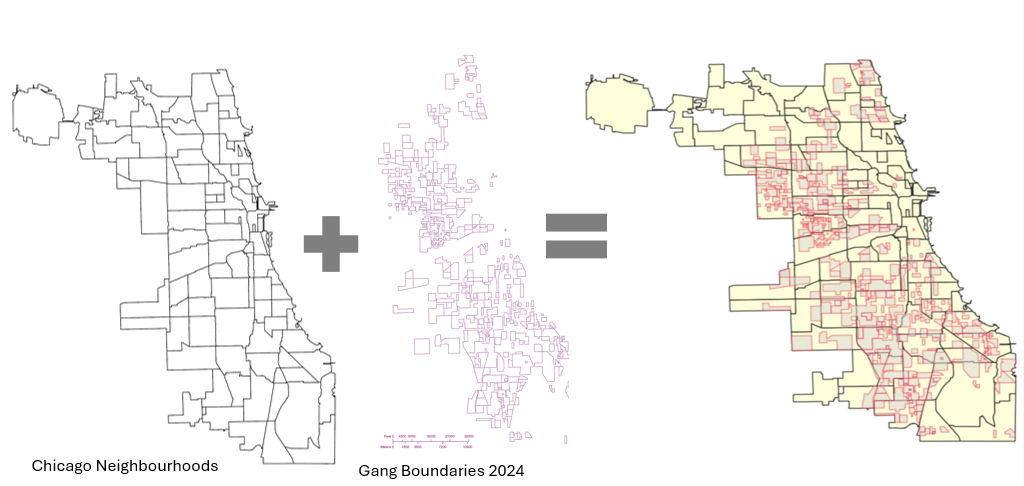
Gang territory boundary polygons overlaid with neighborhood boundaries to enable spatial intersection and proximity analysis (Figure 5).
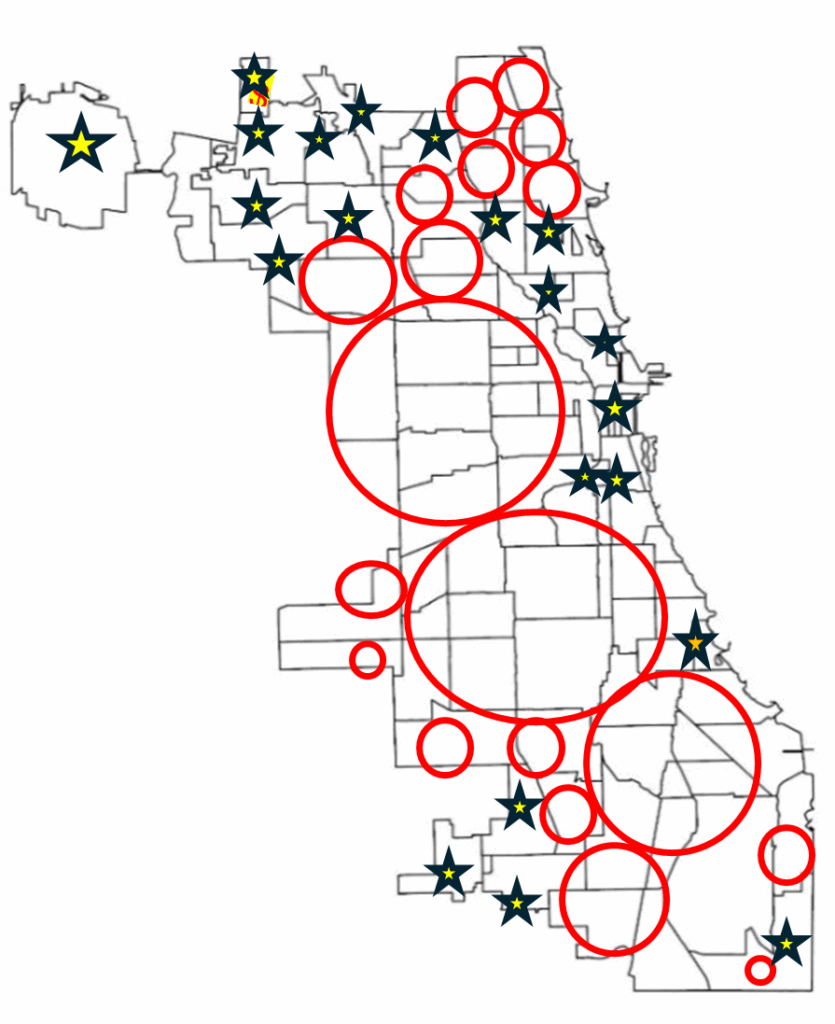
Within ArcGIS Pro, the combined map of both boundaries allowed for analysis of the neighbourhoods with the most gang boundaries. Rough sketch of these neighbourhoods was made by circling the neighbourhoods of a clean map of Chicago, where the bigger circles show the areas with more gang areas and the stars indicate the neighborhoods with no gang boundaries (Figure 6). The CMAP was used to look at the demographics of the neighborhoods with the most area of gangs and compared to the areas with no gang areas (e.g. O’Hare).
SketchUp
SketchUp is 3D modeling tool that is used to generate and manipulate 3D models and is often used in architecture and interior design. Using this software for this project was a different purpose of the software; by importing Chicago neighborhoods outline as an image I was able to trace the neighborhoods.
Step 3: Visualization with 3D Extrusions (Sketch Up)
Determined the highest height of the 3D maps models, was based on the total number of neighborhoods (98) and total number of gangs records/areas (46). Determining which neighbourhoods had the most gang boundaries was based on the gang area number which was provided in the Gang Boundary file. The gang with the most area totaled to shape area of 587,893,900m2, where the smallest shape area is 217,949m2. Similar process was done with neighbourhood area measurements. Neighbourhoods were raised based on the number of gang areas that were present within that neighbourhood (as previously shown in Figure 5). 5’ (feet) is the highest neighbourhood, and 4” (inches) is the lowest neighbourhood where gangs are present, neighbourhoods that do not have gangs are not elevated.
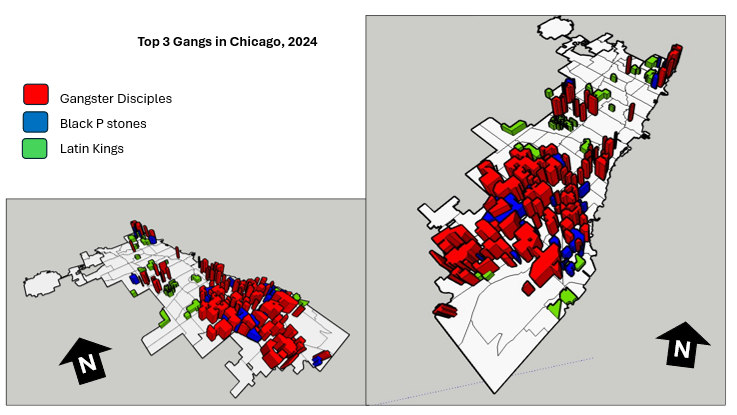
A different approach was applied to the top 3 gangs map model, where the highest remains same in each gang, but are placed in the neighbourhoods that have that gang present. For instance, Gangster Disciples were set at approximately 5 feet (5′ 3/16″ or 1528.8 mm), Black P Stones at almost 4 feet (3′ 7/8″ or 936.6 mm), and Latin Kings at a little over 1 foot (1′ 8 1/4″ or 514.4 mm).
Map Design
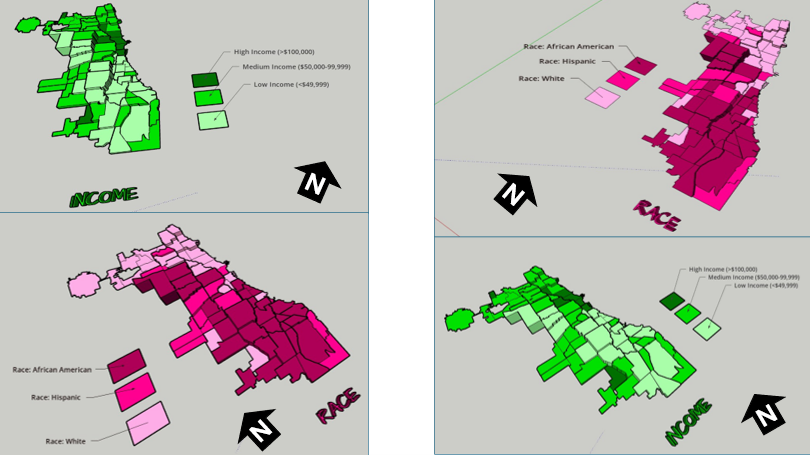
Determined what demographic factors were going to be used to compare with gang areas, for example, income, race, and top 3 gangs (Gangster Disciples, Black P Stones, and Latin Kings). Two elements present with the two demographic maps (height and colour), where colour indicates the demographic factor and the height represents the gang presence (Figure 7).
LIMITATIONS
There was limited information available about the gang areas, which only consisted of gang name, shape area, and length measurements. In terms of SketchUp’s limitations, the free web version as some restrictions, had to manually draw the outline of Chicago neighbourhoods which was time consuming. In addition, SketchUp scale system was complex and was not consistent between maps. To address tis, each corner of the map was measured with the Tape Measure Tool to ensure uniformity. Lastly, when the final product was viewed in augmented reality (AR), the map quality was limited such as the neighbourhood outlines were gone, and the only parts that were visible were the colour parts of the models.
CONCLUSION (Key Insights)
The most visual pattern shown from the race map is the areas with more gang activity have a large population of African Americans (Figure 7). For the income map, indicated in green, more gang areas have lower income whereas the areas with higher income do not have gangs in those neighborhoods. Based on the top three gangs, Gangster Disciples have the most gang boundaries across Chicago neighborhoods (Figure 8). Gangster Disciples takes up 33.6% of the area in km2, founded in 1964 in Englewood.
FINAL PRODUCT
The final product, is user interactive through a QR code that allows viewers to look at the map models using augmented reality (AR) just by pointing your mobile device camera at the QR code below.

Being aware that the quality of the AR has its limits, the SketchUp map models can be viewed using the Geovis Map Models button below.
Reference
Assari, S., Boyce, S., Caldwell, C. H., Bazargan, M., & Mincy, R. (2020). Family income and gang presence in the neighborhood: Diminished returns of black families. Urban Science, 4(2), 29.












